Petroleum industry makes use of many different activities in all the sectors of the business cycle from upstream to downstream. Oil and services company’s managements apply HSE policies to all levels of operations and in all sectors.

HSE, which stands for Health, Safety, and Environment, is a crucial aspect of the oil and gas industry. It refers to a set of principles, guidelines, and practices aimed at protecting the health and safety of employees, contractors, and the environment. Health, Safety, and Environment are separate issues, each with its own technology, but they are often combined in the same functional groups within the oil companies.
These three subjects are of paramount importance to the petroleum industry and adherence to HSE guidelines is a requirement for operators worldwide and is also dictated by internal policies of most corporations.
It is fundamental to have and implement an HSEMS (Health, Safety, and Environmental Management System) which defines the principles by which operations are conducted and control the risks in the whole industry cycle.
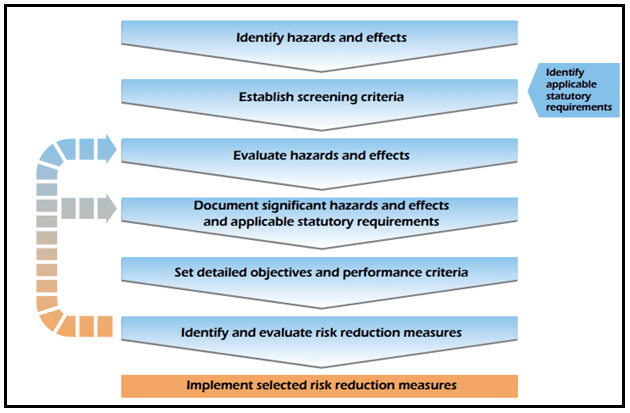
Here are some key concepts related to HSE in the oil and gas industry:
1. Risk Assessment:
Conducting thorough assessments to identify potential risks and hazards associated with various activities, processes, and equipment. This includes analyzing potential consequences and implementing control measures to mitigate risks.
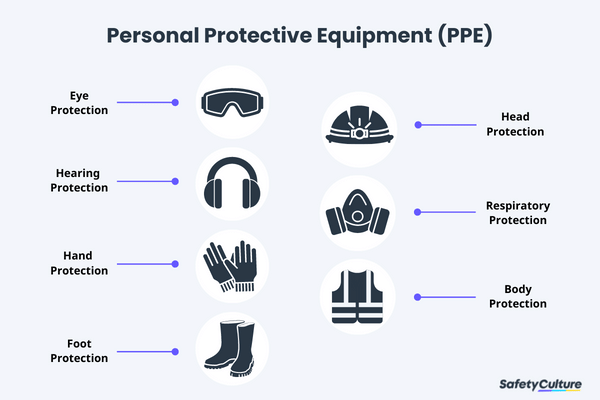
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Ensuring that all workers have access to and properly utilize appropriate PPE, such as helmets, gloves, goggles, and safety shoes, to protect against workplace hazards.
3. Process Safety Management (PSM):
Implementing a systematic approach to managing the integrity of hazardous processes, including the identification and control of potential hazards, emergency response planning, and regular inspections and audits.
4. Safety Culture:
Cultivating a workplace culture where safety is prioritized, and all employees are actively engaged in promoting safe practices. This includes providing adequate training, encouraging reporting of near-misses and incidents, and fostering open communication.
5. Environmental Protection:
Implementing measures to minimize the impact of operations on the environment, such as managing waste disposal, preventing spills and leaks, and complying with environmental regulations.

6. Emergency Response Planning:
Developing comprehensive plans and procedures to effectively respond to emergencies, including fires, explosions, and natural disasters. This involves conducting drills and exercises to ensure preparedness and timely response.
7. Contractor Management:
Ensuring that contractors and subcontractors working on-site adhere to the same HSE standards as employees. This includes conducting pre-qualification assessments, providing necessary training, and monitoring their performance.
8. Occupational Health:
Promoting and maintaining the physical and mental well-being of workers by conducting regular health screenings, providing access to medical facilities, and addressing occupational health risks such as exposure to hazardous substances.

9. Incident Investigation and Reporting:
Establishing a framework for reporting and investigating incidents, near-misses, and potential hazards to identify root causes and implement corrective actions to prevent reoccurrence.
10. Continuous Improvement:
Emphasizing the importance of ongoing evaluation, learning, and improvement of HSE performance through regular audits, reviews, and benchmarking against industry best practices.
These concepts form the foundation for creating a safe and environmentally responsible working environment in the oil and gas industry. Adhering to HSE principles helps protect human life, minimize environmental impact, and ensure the sustainability of operations.
References:
- Oil and gas portal
